DWARF是什么? DWARF (Debugging With Attributed Record Formats)是一种广泛使用的调试信息标准格式,主要用于描述程序源代码与编译后二进制代码之间的映射关系。其核心功能包括:
变量位置跟踪 :记录变量在执行期间的位置变化(寄存器/栈/内存地址)源码映射 :关联机器指令与源代码行号数据类型描述 :存储结构体/数组等复合类型的布局信息
DWARF数据通常存储在可执行文件的.debug_*段中,不加载到程序运行时内存 ,仅由调试器或工具链使用。
如何使用DWARF信息? 使用pyelftools可以轻松获取DWARF信息,比如遍历某个文件的DWARF信息:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 def dwarf_walk_dies (dwarfinfo: DWARFInfo ) -> None : for CU in dwarfinfo.iter_CUs(): top_DIE = CU.get_top_DIE() def walk_die (die, level=0 ): print (' ' * level + f'{die.tag} : {die.get_full_path()} ' ) for child in die.iter_children(): walk_die(child, level+1 ) walk_die(top_DIE)
示例输出:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 DW_TAG_compile_unit: /home/developer/func_enc/func_copy/libtest.c DW_TAG_variable: global_var DW_TAG_base_type: int DW_TAG_base_type: long unsigned int DW_TAG_base_type: unsigned int DW_TAG_base_type: unsigned char DW_TAG_base_type: short unsigned int DW_TAG_base_type: signed char DW_TAG_base_type: short int DW_TAG_base_type: long int DW_TAG_typedef: __pid_t DW_TAG_base_type: char DW_TAG_const_type: DW_TAG_pointer_type: DW_TAG_variable: DW_TAG_subprogram: sleep DW_TAG_formal_parameter: DW_TAG_subprogram: printf DW_TAG_formal_parameter: DW_TAG_unspecified_parameters: DW_TAG_subprogram: getpid DW_TAG_subprogram: test_func DW_TAG_formal_parameter: msg DW_TAG_formal_parameter: count DW_TAG_formal_parameter: ret DW_TAG_variable: c DW_TAG_pointer_type:
或者使用DWARF获取某个变量的位置:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 def dwarf_find_var (dwarfinfo: DWARFInfo, varible: str ) -> None : for CU in dwarfinfo.iter_CUs(): for DIE in CU.iter_DIEs(): if DIE.tag == 'DW_TAG_variable' : name_attr = DIE.attributes.get('DW_AT_name' ) if name_attr and name_attr.value.decode() == varible: loc_attr = DIE.attributes.get('DW_AT_location' ) if loc_attr: loc_expr = loc_attr.value loc_parser = LocationParser(dwarfinfo.location_lists()) loclist = loc_parser.parse_from_attribute(loc_attr, CU['version' ]) for entry in loclist: if hasattr (entry, 'loc_expr' ): ops = entry.loc_expr else : ops = entry expr_parser = DWARFExprParser(dwarfinfo.structs) parsed_ops = expr_parser.parse_expr(ops) if parsed_ops and parsed_ops[0 ].op_name == 'DW_OP_addr' : print (f"{varible} 地址: 0x{parsed_ops[0 ].args[0 ]:x} " ) else : print (f"{varible} 复杂表达式: {parsed_ops} " ) else : print (f"{varible} 没有DW_AT_location" )
示例输出:
1 mask_var 复杂表达式: [DWARFExprOp(op=145, op_name='DW_OP_fbreg', args=[-20], offset=0)]
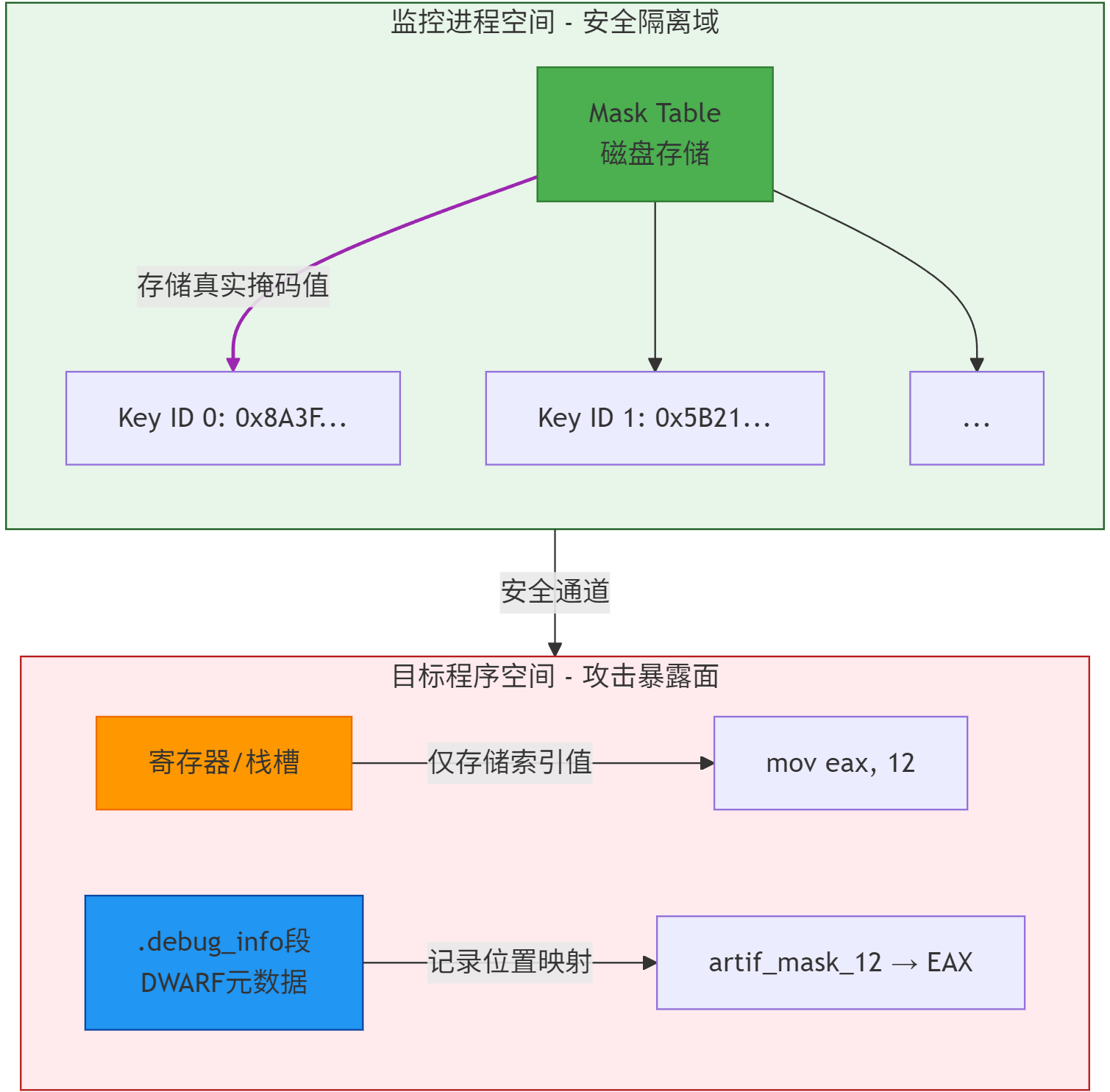
CoDaRR如何利用DWARF? 在CoDaRR
1 编译器为每个数据随机化(DSR)掩码生成人工局部变量 ,比如,为掩码表索引MASK_12创建变量artif_mask_12
2 在DWARF中记录变量在函数执行期间的物理位置:
1 2 3 <0x400>: DW_TAG_variable DW_AT_name: "artif_mask_12" DW_AT_location: DW_OP_reg15 (R15寄存器)
3 动态更新:当重随机化触发时,监控进程解析目标程序堆栈后,通过DWARF定位当前栈帧的所有活跃掩码位置,随后监控进程将所在寄存器中的变量值替换为新掩码值。
安全隔离性:DWARF段永不加载 到目标程序内存,仅监控进程通过/proc/pid/mem接口访问,且DWARF存储掩码表索引而非实际密钥值。
使用LLVM IR插桩掩码变量 目标:
1 对每一个被混淆的代码区域,在入口插入全局变量mask_<size>_<idx>。
2 用DWARF提取该变量的物理地址,和「安全内存」里的掩码表做映射。
3 运行时:程序凭变量地址 → 查表 → 拿到掩码,再做反混淆。
流程:
1 pass插桩(伪代码)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 bool runOnModule (Module &M) override unsigned Idx = 0 ; for (Function &F : M) for (BasicBlock &BB : F) if (isObfuscated (BB)) injectMaskVar (M, BB, Idx++); return true ; }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 void injectMaskVar (Module &M, BasicBlock &BB, unsigned Idx) std::string Name = "mask_" + std::to_string (BB.size ()) + "_" + std::to_string (Idx); GlobalVariable *GV = new GlobalVariable ( M, Type::getInt32Ty (M.getContext ()), false , GlobalValue::ExternalLinkage, 0 , Name); GV->setSection (".dwarf_debug" ); IRBuilder<> Builder (&*BB.getFirstInsertionPt ()); Builder.CreateStore (ConstantInt::get (Type::getInt32Ty (M.getContext ()), 0 ), GV); }
2 使用pyelftools提取地址(见上面例子)
3 运行时链路(伪代码)
1 2 3 4 5 6 extern uint32_t *mask_<size>_<idx>; void deobfuscate () { uintptr_t var_addr = (uintptr_t )&mask_<size>_<idx>; uint32_t mask = secure_mem_lookup(var_addr); xor_code(mask); }


评论区
欢迎你留下宝贵的意见~